Important insect pests and diseases of vegetables and fruits
Potato
> Late blight disease
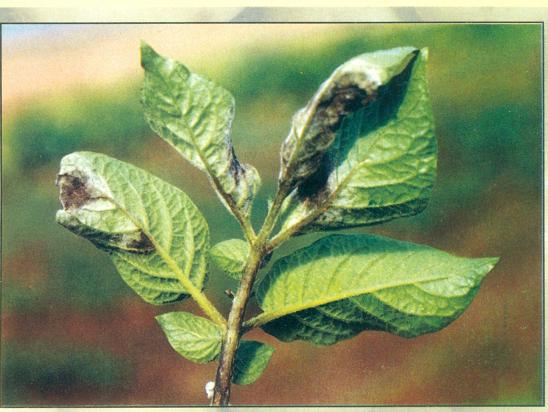

> Symptoms :
Black patches on margins of leaves with whitish fungus growth visible on lower surface in the morning hours. Foliage is killed in a few days if moist weather prevails.Brown depressed patches appear on tubers which finally rot in the soil.
> Management :
i) Use selected healthy tubers for planting. ii) Infected/rejected tubers taken out of cold stores should be burried and not left in the open. iii) Follow high ridge culture to avoid tuber infection. iv) Spray the crop with Antracol/ Indofil M-45/ Kavach @ 500-700g or Copper oxychloride 50 WP @ 750-1000g/ acre in 250-350 litres of water in the first week of November before the appearance of disease followed by 5 more sprays at 7 days interval. Under heavy disease risk situation instead of 3rd and 4th spray of Indofil M - 4 5 / K a v a c h / Antracol, give two sprays of Ridomil Gold or Sectin 60 WG or Curzate M8 @ 700 g or Equation Pro @200 ml per acre at 10 days interval. Subsequently give one spray of Indofil M-45/ Kavach/ Antracol. In late/spring sown crop if the previous crop is infected and disease risk is heavy due to humid weather, give first spray of Ridomil Gold/ Sectin 60 W G/ Curzate M-8@ 500 g or Equation Pro@ 200ml per acre followed by three sprays of Indofil M-45/ Kavach/ Antracol @ 700g per acre at 7 days interval.
Tomato
> Late blight disease

> Symptoms :
Dark water-soaked patches appear on leaves and stem. The fruit is also affected. Crop is rapidly destroyed if rains occur during February.
> Management :
i) Spray the crop with Indofil M-45 @600g/acre at an interval of 7 days during February- March just after rains. ii) When the disease risk is heavy, spray the crop in the middle of February with Ridomil MZ @500g per acre followed by 3 sprays of Indofil M-45 @600g/acre in 200 litres of water at 7 day intervals.
> Root knot nematode
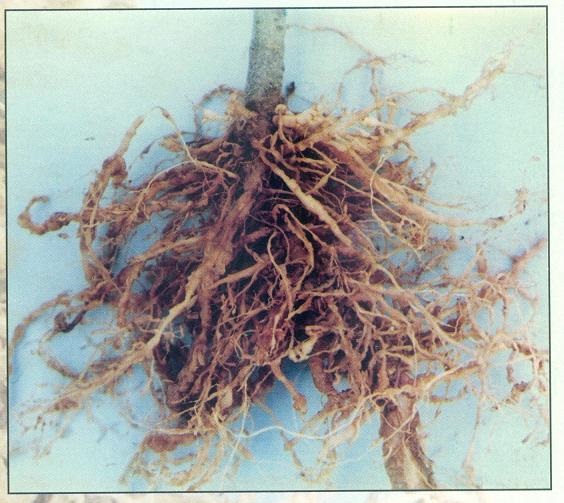
> Symptoms :
Yellowing of leaves, patchy growth of plants with knot like swellings or galls on roots.
> Management :
i) Grow nematode resistant variety Punjab NR-7 in infested fields. ii) Solarize water saturated nursery bed using transparent polythene sheet (50 micron) for 40 days in the months of May- June for the control of root knot nematode in nursery beds. iii) Incorporate 40 days old toria and taramira crops into tomato nursery beds 10 days before sowing and turn the soil 3-4 times before sowing of tomato. iv) Dip the roots of the nursery plants in 0.03% Dimethoate (10ml of Rogor 30 EC in 10 litres of water) for 6 hours before transplanting. v) Grow garlic in root knot nematode infested fields in rotation with other vegetable crops.
Chilli
> Leaf curl disease
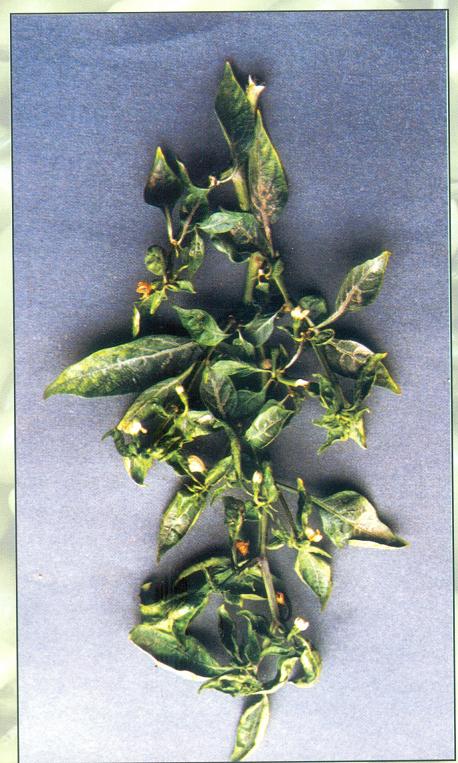

> Symptoms :
Affected plants become stunted and have rosetted appearance and there is yellowing curling of leaves. This virus is transmitted by whitefly.
> Management :
1. Rogue out and destroy the virus infected plants. 2. Spray with 400ml Malathion 50EC in 100-125 litres of water/ acre at 15-20 days interval.
> Mite

> Symptoms :
Mites feed on the underside of young leaves, due to which the leaves become elongated, strap shaped and curled. Their lower surface appears silvery where as the upper surface looks more dark green than the healthy ones.
> Management :
Spray the crop with 400 ml of Malathion 50 EC in 100-125 litres of water at 15-20 days interval.
Pea
> Powdery mildew

> Symptoms :
White floury patches covering large areas, appear on stem, branches, leaves and pods. Seeds of infected plants shrivel and loose taste.
> Management :
Spray the crop with Karathane 40 EC @80ml or Sulfex @600g in 200 litres of water per acre. Three sprays may be given at 10 days interval.
> Wilt & root rot
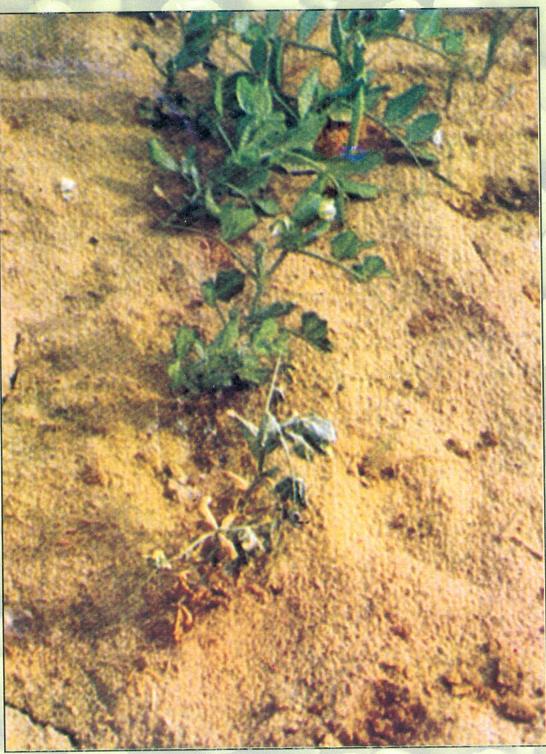

> Symptoms :
Reddish brown cankers may appear on the collar region of the stem. There is rotting of roots which results in poor growth of plant, yellowing of leaves followed by wilting of the plant.
> Management :
i) Avoid early sowing of the crop as it is more susceptible to this disease. ii) Treat the seed with Bavistin @1g or Captan @ 2g or talc based formulation of Pseudomonas fluorescens @15g+1g Captan per kg seed before sowing.
Guava
> Fruit fly
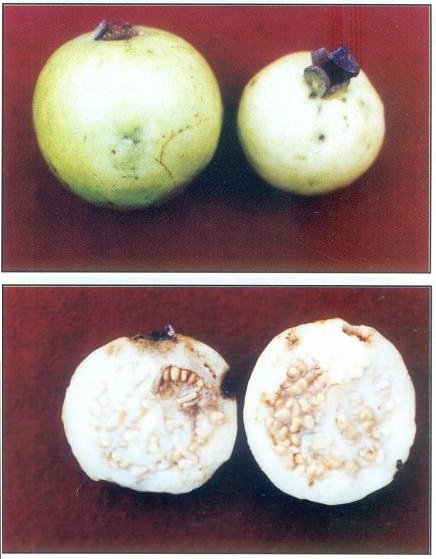

> Symptoms :
It is the most common and serious pest of guava. The infested fruits show depressions with dark green punctures and when cut open the wriggling maggots are seen inside. The infested fruits rot and fall down.
> Management :1. Avoid taking rainy season crop in orchards with history of severe fruit fly infestation. 2. Harvest the ripening fruits timely. 3. Remove the fallen fruits from the ground and bury them at atleast 60 cm depth. 4.Do shallow ploughing with cultivator immediately after harvest for killing the pupating larvae/pupae in soil. 5. In orchards with history of severe fruit fly infestation, Spray 1250 ml Sumicidin 20 EC(fenvalerate) in 500 litres of water at weekly intervals on ripening fruits, starting from July onwards till the rainy season crop is over.
> Shoot borer
> Symptoms :It is serious under nursery conditions. It damages the tender shoots of nursery/adult trees of guava. The quality of the infested seedlings is impaired as the buds below the damaged portion produce lateral shoots and plants give a bushy look. Secondly, the infested shoots dry up and a fine black frass is visible on the leaves/shoot parts beneath the site of infestation.
> Management :In nursery, spray 500 ml Durmet 20 EC (chlorpyriphos) or 400 ml Ekalux 25 EC (quinalphos) per acre in 100 litres of water.
> Wilt disease

> Symptoms :
Symptoms appear on the infected trees many months after their roots are attacked by the fungi. Sparse foliage, denuded branches, yellowing of leaves and wilting are the important symptoms. In the root, the cambium in between the bark and the wood, shows discoloration. Replanted trees bear fruit for a number of years before ultimately succumbing to the disease.
> Management :(i) Plant guava in a well drained field. Avoid too heavy soils. (ii) Uproot and burn the wilted trees along with their roots. (iii) Drench the soil in the pit with 2 per cent Formalin solution and cover with sarkanda and old wetted gunny bags. Expose the soil for 14 days and replant healthy guava plants.
> Zinc deficiency

> Symptoms :
The affected plants produce small leaves with yellowing or chlorosis in between the veins. The plant growth is suppressed and dieback of the branches is observed.
> Management :This deficiency can be corrected by spraying the trees with zinc sulphate-lime mixture (1 kg of zinc sulphate + half kg of unslaked lime in 100 litres of water). Give 2 or 3 such sprays at fortnightly interval between June to September.
Ber
> Powdery mildew disease

> Symptoms :
Young developing leaves and fruits are covered with whitish powdery mass of the fungus. This condition results in premature defoliation and fruit drop. Fruits remain small and become cankered and cracked.
> Management :Spray 0.25 per cent wettable sulphur (250 g in 100 litres of water) or 0.05% Karathane 40EC (50 ml in 100 litres of water) or 0.05% Bayleton 25 WP (50g in 100 litres of water) in September (at flowering), mid October, mid-November and mid- December. An another spray can be given if need arises in January.
> Fruit fly
> Symptoms :
The infested fruits become deformed, turn brown, rot and drop off. Fully grown maggots emerge out of the fruit by making a hole and pupate in the soil.
> Management :I. Pick and destroy the infested fruits. II. To escape egg laying on fruits, harvest at green and firm stage and do not allow the fruit to ripe on the tree. III. Rack the soil around the trees during summer to expose the pupae to heat and natural enemies. IV. Spray 500 ml Rogor 30 EC (dimethoate) in 300 litres of water during February-March.